
Zero-Trust Architecture: Redefining Network Security
By Ankita Das

80% of data breaches occur due to compromised credentials. Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA) is transforming network security by eliminating implicit trust. This model emphasizes strict identity verification for every user and device, regardless of location. Traditional security methods often fail in today’s cloud-centric world, necessitating a paradigm shift. ZTA reduces the attack surface, preventing unauthorized access and lateral movement within networks. Organizations adopting ZTA can enhance their security posture while enabling seamless resource access. As cyber threats evolve, so must our defenses, making zero-trust principles essential for modern cybersecurity strategies. Scroll down to learn more about Zero-Trust Architecture principles and benefits.
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
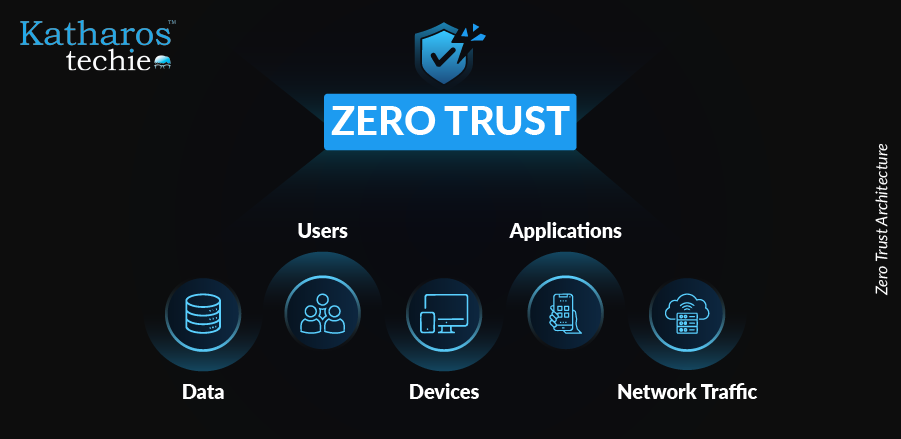
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a security framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This approach assumes that threats can originate inside and outside the network. The core principles of ZTA include strict identity verification, least-privileged access, and continuous monitoring.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. implemented Zero Trust Architecture to enhance cybersecurity, better protecting sensitive financial data. Similarly, Goldman Sachs adopted ZTA to enforce continuous verification and strict access controls, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. These implementations demonstrate ZTA’s effectiveness in safeguarding critical data across the financial sector.
These successful implementations underscore the foundational principles of Zero Trust Architecture, which prioritize security at every level of an organization. The five pillars of ZTA are:
- Identity: Focuses on managing user identities with least-privileged access.
- Devices: Ensures the integrity of devices accessing services and data.
- Networks: Aligns network segmentation with application workflows to minimize implicit trust.
- Applications and Workloads: Integrates security measures closely with application workflows.
- Data: Emphasizes a data-centric approach to cybersecurity by identifying and categorizing data assets.
These pillars play a critical role in tightly controlling and continuously verifying access. Together, they create a comprehensive strategy that enhances security, mitigates risks, and protects sensitive information across the organization. Now that we know what Zero Trust Architecture is and its core principles, let’s understand the need for implementing this security framework across industries.
The Need for Zero Trust Architecture
The increasing frequency of cyberattacks highlights the necessity for Zero Trust Architecture. In 2023 alone, 80% of organizations reported experiencing a data breach of data stored in the cloud. Traditional perimeter-based security models are insufficient as users access applications from diverse locations.
Organizations are increasingly shifting towards cloud services, making it essential to secure access effectively. For instance, NTT DATA transitioned from traditional VPN-based security to a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) following significant challenges with remote access management. This shift allowed them to verify user identities and device states regardless of location. It also helped the organization enhance security for its global workforce.
Furthermore, the rise of remote work has expanded the attack surface significantly. By implementing ZTA, organizations can ensure that every access request is scrutinized in real-time. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances overall security posture.
Comparison: Zero Trust Architecture vs Traditional Security Models
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, the need for effective security measures becomes paramount. Traditional security models that rely heavily on perimeter defenses are no longer effective against modern threats. Here’s the comparison between Zero Trust Architecture and traditional security models, highlighting their key differences:
| Feature | Zero Trust Architecture | Traditional Security Models |
| Trust Model | Never trust; always verify | Implicit trust within the network perimeter |
| Access Control | Least-privileged access | Broad access based on network location |
| Monitoring | Continuous monitoring | Periodic checks |
| Response to Threats | Real-time response | Delayed response |
| Data Protection | Data-centric approach | Network-centric approach |
How Does Zero Trust Architecture Work?
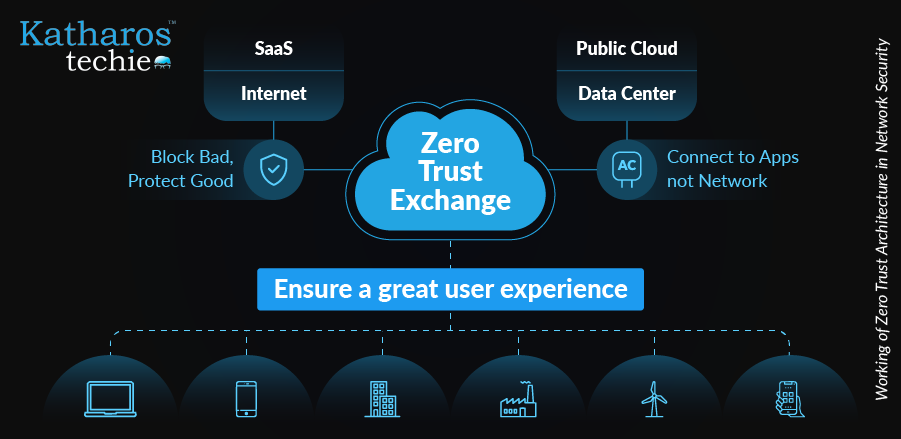
Zero Trust Architecture operates on three fundamental steps: verifying identity and context, controlling risk, and enforcing policy. First, every connection request undergoes verification to assess user identity and context. This process involves understanding who is requesting access and from where.
Next, risk control measures are applied based on the verified identity and context. For example, the system activates additional verification steps when an employee attempts to access sensitive data from an unfamiliar device or location.
Finally, policy enforcement occurs based on a calculated risk score. If deemed safe, a secure connection is established; otherwise, access is denied. A real-world example includes a major tech company that adopted ZTA to enhance its security framework. They reported reduced unauthorized access attempts due to continuous monitoring and real-time verification processes.
Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust Architecture

Organizations like Microsoft, Akamai, and Accenture are increasingly adopting ZTA frameworks to address the complexities of modern cybersecurity. This model is particularly effective in securing access to cloud services and protecting sensitive data from evolving threats. Here are the key benefits of implementing Zero Trust Architecture:
- Enhances Overall Security: Zero Trust Architecture minimizes implicit trust by requiring verification for every access request. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even from trusted devices. It also continuously monitors user behavior to identify suspicious activities, allowing for rapid responses to potential threats.
- Boosts Hybrid Workforce Productivity: As remote work becomes prevalent, organizations must ensure secure access to resources. Zero Trust allows employees to access necessary applications from any location while maintaining security.
- Protects Data and Applications from Cyber Threats: ZTA reduces the risks of data breaches and insider threats by implementing strict access controls. Organizations can implement fine-grained authorization policies to ensure that only authorized users access sensitive data.
- Supports Compliance Initiatives: Zero Trust simplifies compliance with regulatory standards by providing detailed logs of user activities and access requests. This transparency aids audits and ensures organizations meet requirements like GDPR and HIPAA. A government agency using ZTA reported improved compliance audit results due to enhanced visibility into data access.
- Improves Monitoring and Alerting: Continuous monitoring within a Zero Trust framework allows organizations to detect anomalies in real-time. Its advanced tools analyze user behavior and system interactions, providing actionable insights for security teams. This proactive approach leads to quicker incident response times, enhancing overall security posture.
Zero-Trust Architecture offers significant benefits that extend beyond immediate security improvements. By minimizing implicit trust, organizations can greatly reduce unauthorized access risks. As remote work grows, ZTA enables secure access to applications, enhancing employee productivity. Its strict access controls protect sensitive data from breaches and insider threats while ensuring regulatory compliance. Integrating emerging technologies like AI and ML will further enhance Zero Trust frameworks. Thus, allowing organizations to adapt to evolving cyber threats and boost their security posture.
This wraps up our take on Zero-Trust Architecture, its principles, workings, and benefits. As we conclude, it is safe to say that ZTA is crucial for modern cybersecurity strategies in an ever-changing threat environment. So, are you ready to prioritize this model to safeguard your assets effectively? Embrace zero-trust principles today to strengthen your network security against potential breaches.