
Top 9 Cybersecurity Trends in 2024: What You Need to Know
By Ankita Das

The top 9 cybersecurity trends for 2024 highlight the evolving landscape of digital threats that organizations must watch out for. Cybersecurity is a multifaceted field crucial to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining operational integrity across various sectors. As cyber threats continue to grow, organizations must prioritize the development of robust cybersecurity frameworks and invest in comprehensive training programs. Together, these measures will significantly enhance their ability to protect against breaches effectively.
The cybersecurity landscape is always changing, with cybercriminals constantly devising new tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. This dynamic environment presents significant challenges for the industry, particularly the acute shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals. As of 2023, it is projected that there will be a global shortfall of 4 million jobs in this critical field, underscoring the urgent need for skilled talent to combat increasingly sophisticated threats.
Additionally, emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) introduce new complexities that require advanced security measures. For instance, attackers are using AI to automate complex attacks, underscoring the urgent need for organizations to enhance their defenses. As organizations adapt to these challenges, a proactive approach to cybersecurity will be essential for maintaining resilience in an ever-changing threat landscape.
Moving ahead in the future, understanding these trends will be essential for organizations aiming to bolster their cybersecurity measures and mitigate risks associated with the next wave of threats.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is an essential discipline to protect internet-connected systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. With the rapid expansion of technology and digital infrastructure, its importance has escalated significantly. A report from Cybersecurity Ventures projects that global cybercrime costs will reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Thus, indicating the severe financial implications of inadequate cybersecurity measures.
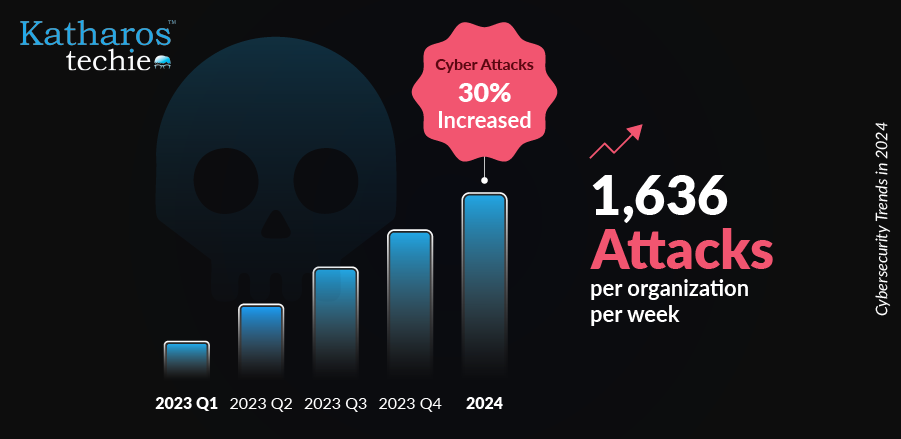
Cyber threats fall into various categories, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and data breaches. Ransomware attacks, such as the notorious WannaCry incident in 2017, affected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries. As a result, it was causing estimated damages of $4 billion. Data breaches have also become a critical concern; for instance, the 2017 Equifax breach compromised the sensitive information of approximately 147 million individuals, highlighting vulnerabilities in data protection practices.
Top 9 Cybersecurity Trends in 2024

As we move into 2024, the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing threats. Here are the top 9 trends shaping the future of cybersecurity.
1. Increased Focus on AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into cybersecurity strategies is becoming increasingly vital. Organizations are leveraging these technologies to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data at speeds unattainable by human analysts, identifying patterns that indicate potential security breaches. According to a report, the market for AI in cybersecurity is projected to surpass $102 billion by 2032, with an estimated value of $24.8 billion in 2024.
Moreover, AI and ML can automate routine security tasks, allowing cybersecurity professionals to focus on more complex threats. For example, Darktrace employs AI to create an “immune system” for networks, autonomously identifying and mitigating threats in real-time. However, AI also presents challenges; adversaries are utilizing AI to develop more sophisticated attacks, fueling a continuous arms race between defenders and attackers.
2. Zero Trust Cyber Security
The Zero Trust security model has gained significant traction as organizations recognize the limitations of traditional perimeter-based defenses. The core principle of Zero Trust is “never trust, always verify,” which mandates strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter. According to a 2024 report from TechTarget, over two-thirds of organizations are implementing Zero Trust policies.
The Zero Trust framework enhances security by enforcing least-privilege access controls and continuous monitoring of user behavior. For instance, if an employee typically accesses company resources from a specific location but suddenly attempts to log in from another country, the Zero Trust model would trigger additional authentication measures. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes potential damage from breaches by isolating compromised accounts or devices.
3. Evolution of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks continue to evolve in sophistication and prevalence, posing significant risks to organizations. In 2023 alone, APWG observed almost five million phishing attacks, making it the worst year for phishing on record. Attackers are now employing advanced tactics such as spear phishing and whaling, targeting specific individuals within organizations with personalized messages that appear legitimate.
Furthermore, the rise of deepfake technology has introduced new dimensions to phishing attacks. Cybercriminals can use deepfake audio or video to impersonate trusted individuals within an organization, making it increasingly challenging for employees to differentiate genuine requests from deceptive ones. As a result, organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs that educate employees about recognizing phishing attempts and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) as an additional layer of defense.
4. Growing Importance of IoT Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has created new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals are eager to exploit. By 2024, it is estimated that there will be over 30 billion connected IoT devices worldwide, each representing a potential entry point for attackers. Many IoT devices lack robust security features, making them easy targets for exploitation.
Organizations must prioritize IoT security by implementing stringent access controls and regular firmware updates. For example, in 2023, a large-scale attack on unsecured IoT devices led to significant data breaches across multiple industries. To reduce these risks, businesses should implement a robust IoT security strategy that incorporates network segmentation to keep IoT devices separate from critical systems and continuous monitoring to detect any unusual activity.
5. Attacks Against Cloud-based Services
As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, cybercriminals are shifting their focus toward cloud-based services. In 2023, cloud-related incidents surged by over 50%, with attackers exploiting misconfigurations and vulnerabilities in cloud environments. To reduce these risks, businesses should implement a robust IoT security strategy that incorporates network segmentation to keep IoT devices separate from critical systems and continuous monitoring to detect any unusual activity.
To combat these threats, organizations must adopt best practices such as regular audits of cloud configurations and implementing robust identity management solutions. For instance, in early 2023, a major data breach occurred due to an improperly configured cloud storage bucket that exposed sensitive customer information. Continuous education on cloud security best practices is essential for teams managing cloud resources.
6. Expansion of Remote Work
The shift towards remote work has transformed how organizations approach cybersecurity. Traditional security measures are no longer adequate as employees access corporate networks from multiple locations and devices. A survey conducted by Gartner revealed that 88% of organizations have encouraged or required employees to work remotely since the onset of the pandemic.
This trend necessitates enhanced security measures such as VPNs and endpoint protection solutions tailored for remote work environments. Additionally, businesses must implement policies governing acceptable use and conduct regular training sessions on secure remote work practices. The rise in remote work has also resulted in targeted attacks on home networks; therefore, organizations must ensure that employees have the tools and knowledge to secure their home office setups effectively.
7. State-Sponsored Warfare
State-sponsored cyber warfare is becoming more prevalent as nations leverage cyber capabilities for espionage and disruption. These attacks often target critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, healthcare, and finance. For instance, the 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack demonstrated how a cyber incident could halt fuel supplies across the Eastern United States, leading to widespread panic and economic repercussions. Similarly, attacks on healthcare systems during the COVID-19 pandemic compromised sensitive patient data and disrupted essential services.
Governments must collaborate with private sectors to enhance resilience against these threats through information sharing and joint exercises simulating cyberattack scenarios. For instance, the SolarWinds attack demonstrated how sophisticated state-sponsored actors could infiltrate supply chains and compromise numerous organizations simultaneously. As geopolitical tensions rise, investment in national cybersecurity strategies will be crucial for protecting against state-sponsored threats.
8. Enhanced Focus on Mobile Security
With the increasing reliance on mobile devices for business operations comes a heightened focus on mobile security. A recent report from Kaspersky indicates that mobile malware attacks surged significantly in 2023, with the total number of attacks reaching approximately 33.8 million, marking an increase of 50% compared to the previous year. Cybercriminals take advantage of weaknesses in mobile applications and operating systems to access sensitive data without authorization.
To tackle these challenges, organizations should deploy robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions to enforce security policies across all mobile devices connected to their networks. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be required to access corporate resources via mobile devices. By adopting these measures, businesses can significantly reduce the risk associated with mobile device usage while ensuring employee productivity remains unaffected.
9. Cybersecurity Skill Gap and Education
The cybersecurity skills gap remains a pressing issue as organizations struggle to find qualified professionals amid rising cyber threats. According to (ISC)²‘s Cybersecurity Workforce Study published in early 2024, there is an estimated shortfall of over 4 million cybersecurity professionals globally. This shortage hampers organizations’ ability to defend effectively against sophisticated attacks.
To bridge this gap, companies must invest in training programs that upskill existing employees while promoting cybersecurity education at the grassroots level through partnerships with educational institutions. Initiatives such as internships and mentorship programs can help cultivate new talent entering the field. Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous learning within organizations will ensure that cybersecurity teams remain up-to-date with emerging trends and technologies essential for effective threat mitigation.
In conclusion, as we navigate through 2024, understanding these cybersecurity trends will be crucial for organizations aiming to strengthen their defenses against evolving threats while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.