
The Rise of Edge Computing in Data Processing
By Ankita Das

Edge computing in data processing has evolved from content delivery networks to meet the growing demands of modern data processing. As the proliferation of IoT devices generates vast amounts of data, traditional cloud computing faces limitations in latency and bandwidth. Edge computing addresses these challenges by processing data closer to its source. As a result, it enhances efficiency and enables real-time responsiveness across various applications.

This shift is reflected in the projected growth of the global edge computing market, which is expected to reach $350 billion by 2027. This expansion is driven by its increasing adoption across various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. Edge computing offers substantial benefits such as reduced latency and improved security for sensitive data. However, it also presents challenges, including device management complexity and potential security vulnerabilities.
As organizations increasingly rely on edge computing for critical operations, balancing its advantages with these limitations becomes essential. Encouraging the adoption of edge computing can lead to enhanced operational efficiencies and innovative applications. Nevertheless, careful consideration of security measures and management strategies is necessary to mitigate risks. With that, let’s explore what edge computing is, and how it differs from cloud and fog computing. We will also examine how to effectively harness its benefits while addressing its limitations in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing by shifting computation closer to the source of data generation. This paradigm significantly enhances performance and efficiency, particularly for real-time insights applications. For instance, in autonomous vehicles, processing data at the edge allows for immediate decision-making. This helps reduce response times to less than 10 milliseconds, critical for safety and navigation.
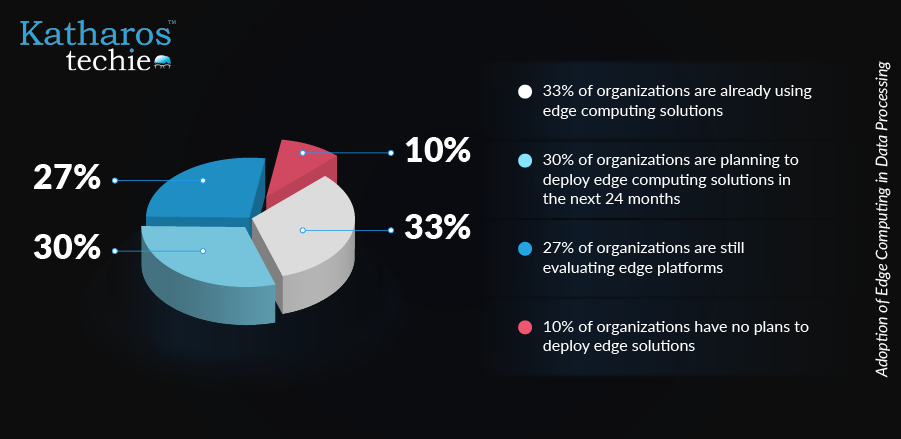
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has led to an explosion of data, with Gartner predicting that by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will originate outside traditional data centers. This shift necessitates a more efficient approach to data management, as conventional cloud computing struggles with bandwidth limitations and latency issues. Edge computing addresses these challenges by enabling localized data processing. Additionally, it enhances security by keeping sensitive data closer to its source, thus minimizing exposure during transmission. This localized processing reduces the risk of data breaches and aids data privacy regulations.
How does Edge Computing Work and How Does It Differ from Cloud and Fog Computing?
Edge computing, fog computing, and cloud computing are three distinct paradigms in data processing, characterized by their unique features, benefits, and optimal applications. These concepts share a theme of distributed computing and resource deployment related to data generation. However, they should be used in a variety of ways due to their differing operational models. Recognizing these differences is essential for organizations to enhance their data management strategies.
The following table summarizes the key aspects of edge, fog, and cloud computing across various dimensions:
| Aspects | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing | Fog Computing |
| Latency | Low latency, ideal for real-time applications | Higher latency due to distance | Moderate latency, closer to the edge than the cloud |
| Data Processing | Localized processing on edge devices | Centralized processing | Aggregates data from multiple edges before sending it to the cloud |
| Use Cases | 1. Autonomous vehicles 2. Industrial automation 3. Real-time monitoring | 1. Big data analytics 2. Collaborative tools 3. Data Backup | 1. Complex IoT environments 2. Surveillance 3. Retail |
| Scalability | Limited by local resources | Highly scalable | Scalable across distributed networks |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduces bandwidth by sending only essential data to the cloud | High bandwidth usage due to data transmission to and from the cloud | Optimizes bandwidth by preprocessing data before sending it to the cloud |
| Security | Enhanced security by keeping sensitive data local | Vulnerable during data transmission | Provides additional security layers between edge and cloud |
Having explored the distinctions between edge, cloud, and fog computing, let’s delve into the compelling benefits of edge computing for data processing. Understanding these advantages can empower organizations to optimize operations and effectively harness real-time data for improved decision-making.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Data Processing

Edge computing offers several significant benefits that enhance data processing and operational efficiency across various industries. These advantages position edge computing as a key technology for organizations aiming to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world. Here are some key advantages:
1. Reduced Latency
By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel to centralized servers. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, where delays can lead to critical failures.
2. Improved Data Security
Edge computing enhances security by keeping sensitive data local, reducing the risk of interception during transmission. This localized processing helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations. It also mitigates potential cyber threats, as less data travels over vulnerable networks.
3. Cost Savings
By minimizing the amount of data sent to the cloud, edge computing reduces bandwidth costs significantly. Organizations can save on cloud service fees and optimize their infrastructure investments by handling data processing locally. This consequently leads to lower overall operational costs.
4. Enhanced Reliability
Edge computing’s decentralized architecture increases system reliability. If one edge device fails, others can continue functioning without disruption. This ensures the continuous availability of critical services and reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
5. Real-Time Insights
With edge computing, businesses can gain immediate access to critical information without the delays associated with cloud processing. This capability allows for faster decision-making and improved operational efficiency. Functionalities like these are particularly helpful in the manufacturing and healthcare sectors.
6. Scalability
Edge computing systems can easily scale to accommodate growing data demands. It generally works by adding new devices or nodes without overhauling centralized infrastructure. This flexibility supports the increasing number of IoT devices and applications.
This concludes our exploration of edge computing benefits. Now, let’s delve into its applications across different industries. Understanding these applications reveals how technology transforms data processing and enhances decision-making capabilities.
Applications of Edge Computing in Data Processing
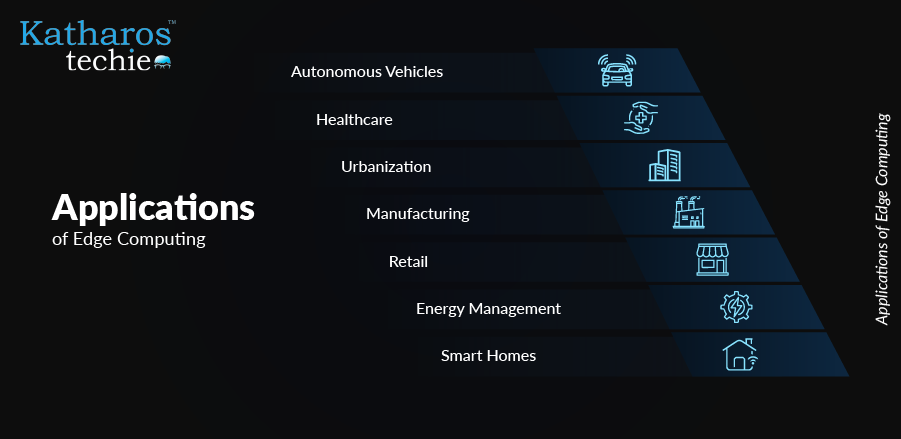
As edge computing continues to evolve, its applications help transform various industries by enabling real-time data processing and decision-making. This technology is particularly impactful where immediate responses are critical. Thus, allowing organizations to harness the power of data generated at the edge. Below are some of the most significant applications of edge computing across different sectors:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are among the most prominent applications of edge computing. These vehicles generate an enormous amount of data—over 40 terabytes per hour—from sensors and cameras that require immediate processing to ensure safety and efficiency. Edge computing allows for real-time data analysis, enabling features like collision avoidance and lane departure warnings to function effectively. For instance, Tesla utilizes edge computing to process data from its fleet of vehicles, allowing for continuous improvements in self-driving algorithms without relying solely on cloud connectivity.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, edge computing facilitates remote patient monitoring through wearable devices and smart medical equipment. By processing health data locally, healthcare providers can receive instant alerts about critical changes in a patient’s condition, significantly reducing response times. A study indicated that digital health intervention can decrease hospitalization rates within 30 days of discharge by 52%. Companies like Philips have implemented edge computing solutions to enhance patient care by enabling real-time monitoring of vital signs and health metrics.
3. Smart Cities
Edge computing is essential for the development of smart cities, where it processes data from various IoT devices such as traffic lights, surveillance cameras, and environmental sensors. This localized processing allows city officials to make real-time decisions that improve urban mobility and public safety. For example, Barcelona uses edge computing to optimize traffic flow by adjusting traffic signals based on current conditions, resulting in a 20% reduction in travel time for commuters.
4. Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, edge computing enhances operational efficiency through predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of machinery. By analyzing data from sensors on the factory floor, manufacturers can identify potential issues before they lead to costly downtime. Companies like GE have adopted edge solutions to monitor equipment health and optimize production processes.
5. Retail
Retailers leverage edge computing to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. By processing data from in-store sensors and customer interactions in real time, retailers can optimize inventory management and personalize marketing efforts. For example, Walmart employs edge computing to analyze shopping patterns instantly, leading to a 10-15% increase in sales through targeted promotions and improved product placements.
6. Energy Management
Edge computing is revolutionizing energy management by optimizing the operation of power grids through real-time data processing from smart meters and other sensors. This technology enables energy companies to manage electricity flow more efficiently, reducing waste and improving sustainability. Pacific Gas and Electric implemented edge solutions that resulted in a 15% reduction in energy consumption during peak hours.
7. Smart Homes
In smart homes, edge computing enables seamless interaction between IoT devices like smart thermostats, security systems, and appliances. By processing commands locally, these devices can respond instantly without relying on cloud connectivity. This capability not only enhances user experience but also improves security by keeping sensitive data within the home network.
This wraps up our exploration of edge computing applications, showcasing its transformative impact across various industries. However, as we look ahead, it’s crucial to consider edge computing challenges. Staying informed about the limitations of the technology can help organizations thoughtfully navigate the complexities and unlock their full potential.
Challenges of Edge Computing in Data Processing

While edge computing offers significant advantages, it also poses unique challenges that require careful consideration. Staying informed about these challenges will enable tech enthusiasts to harness Edge’s full potential while mitigating associated risks. Here are some of the key challenges associated with edge computing:
1. Security Vulnerabilities
IoT devices often operate in less secure environments compared to centralized data centers, making them more susceptible to physical tampering and cyberattacks. The distributed nature of edge computing expands the attack surface, as each device can be a potential entry point for hackers. For example, a botnet attack in 2017 targeted over 5,000 IoT devices on a university campus, exploiting weak passwords and inadequate security measures. Ensuring robust security protocols for each edge device is essential to mitigate these risks.
2. Data Management Complexity
The proliferation of edge devices leads to significant data management challenges. As organizations deploy more devices, tracking and monitoring them becomes increasingly complex. This “data sprawl” can result in bandwidth overcrowding and increased latency, jeopardizing the performance of applications relying on real-time data processing. Developers must implement effective data governance strategies to manage this complexity and ensure that data flows efficiently between edge devices and centralized systems.
3. Connectivity Challenges
Edge computing relies heavily on stable network connections to transmit data between edge devices and centralized systems or cloud services. However, many edge environments may experience intermittent connectivity issues due to their remote locations or reliance on wireless networks. This unreliability can disrupt real-time processing capabilities and lead to data loss or inconsistencies in analytics.
4. Maintenance and Updates
Managing a distributed network of edge devices introduces significant maintenance challenges. Each device may have unique software requirements, necessitating regular updates and patches to ensure security and performance. According to industry reports, 60% of organizations struggle with keeping their edge devices updated due to their dispersed nature. Implementing centralized management solutions can help streamline this process but may also introduce additional complexity.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Issues
As edge computing often involves processing sensitive data, organizations must navigate various compliance and regulatory frameworks that govern data privacy and protection. The decentralized nature of edge computing complicates compliance efforts, as data may be stored and processed across multiple locations with differing regulations. For instance, healthcare organizations must ensure that patient data processed at the edge complies with HIPAA regulations while also managing the risks associated with data breaches.
6. Limited Resources
Edge devices often have constrained computational power and storage capacity compared to traditional cloud infrastructures. This limitation can hinder the deployment of advanced analytics and machine learning models that require substantial resources for processing large datasets. Developers need to optimize algorithms for edge environments, ensuring they can run efficiently within the constraints of these devices.
Edge computing is no longer just a technological trend; it’s a critical component for success in today’s data-driven landscape. It benefits the organization by reducing latency, enhancing security, and improving operational efficiency. Thus, making it essential for industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. But is your edge strategy robust enough to navigate the potential challenges? Begin evaluating your edge computing framework today. Implement best practices such as effective device management, rigorous security protocols, and compliance with data regulations. Don’t wait for a crisis to act—embrace the power of edge computing now to protect your data and drive innovation in your organization.