
The Evolution of Extended Reality (XR)
By Ankita Das

Extended Reality (XR) represents a transformative convergence of technologies that blend physical and digital realities. It encompasses Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). The evolution of XR can be traced back to early innovations such as the Sensorama in 1957 and the Sword of Damocles in 1968, marking the starting point for creating immersive experiences. The term “Extended Reality” emerged later to encapsulate the spectrum of immersive technologies.
XR is rapidly evolving and finding applications across diverse sectors, including gaming, healthcare, education, and manufacturing. Forecasts predict continued expansion, driven by technological improvements like 5G and the integration of digital twins. This will further enable sophisticated real-time simulations and monitoring within virtual environments. As XR technologies mature, they hold the potential to revolutionize human-computer interactions and transform industries. Join us in exploring exciting applications, benefits, and groundbreaking future trends of XR.
What is Extended Reality?
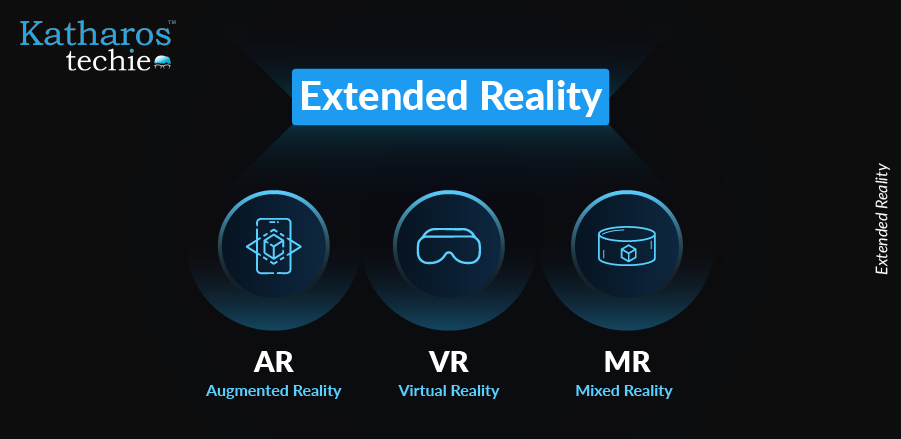
Extended Reality (XR) is an overarching term encapsulating all technologies that enhance or replace our perception of reality. It exists on a spectrum, bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds. This spectrum includes Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in entirely simulated environments; Augmented Reality (AR), which overlays digital information onto the real world; and Mixed Reality (MR), which blends real and virtual objects, allowing them to interact in real-time.
The concept of XR began with the development of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies in the 20th century. Early attempts to create immersive experiences involved innovations such as the Sensorama (1957) and the first head-mounted display (HMD) called The Sword of Damocles (1968). The origins of Extended Reality date back to the 1800s when stereoscopes manipulated viewers’ brains into seeing images in 3D.
In 1838, scientist Sir Charles Wheatstone outlined the concept of “stereopsis” or “binocular vision” where the brain combines two images (one from each eye) to make a single 3D image. This led to the development of the first stereoscopes, devices that took a pair of images and turned them into a 3D image with the illusion of depth. Later in 1935, American science fiction writer Stanley Weinbaum published Pygmalion’s Spectacles. This publication revolves around the main character exploring a fictional world using a pair of goggles, marking an early prediction of VR.
Today, XR is used across sectors like manufacturing and healthcare. In 1956, Morton Heilig’s Sensorama was the first VR machine. It combined 3D video, audio, smells, and vibration. In 1968, Ivan Sutherland created the first AR headset. Called “The Sword of Damocles”, it enhanced the user’s perception. Microsoft’s 2016 HoloLens took AR further with interactive experiences. Also in 2016, Pokémon GO brought AR into the mainstream.
Use Cases of Extended Reality Across Industries
Extended Reality (XR) technologies are transforming industries by enhancing various processes, from design and training to customer experience and collaboration. The following table highlights some prominent use cases of XR across diverse sectors:
| Industry | Use Cases | Examples |
| Biomedical | Interactive education platforms | VR and AR are used in classrooms to teach cell biology and visualize surgical data. |
| Retail | Furniture visualization | The IKEA Place app lets users see how furniture fits in their home before buying. |
| Military | Training and simulation | Headlight headset (1961) was the first VR headset with motion tracking, designed for military use. |
| Entertainment | Gaming and immersive experiences | VR arcade games in the 1990s introduced XR to a new generation. |
| Manufacturing | Training, design, and remote collaboration | XR technologies aid in visualizing designs and training employees. |
| Education | Interactive learning and virtual field trips | Students can experience virtual tours and engage with 3D models. |
| Healthcare | Surgical training, patient education, and therapy | XR helps surgeons practice complex procedures and allows patients to understand treatments. |
| Construction | Training and safety simulations | XR provides realistic training scenarios for construction workers. |
| Law Enforcement | Training simulations for de-escalation and crisis management | XR helps officers train in realistic, controlled environments. |
Advantages of Extended Reality
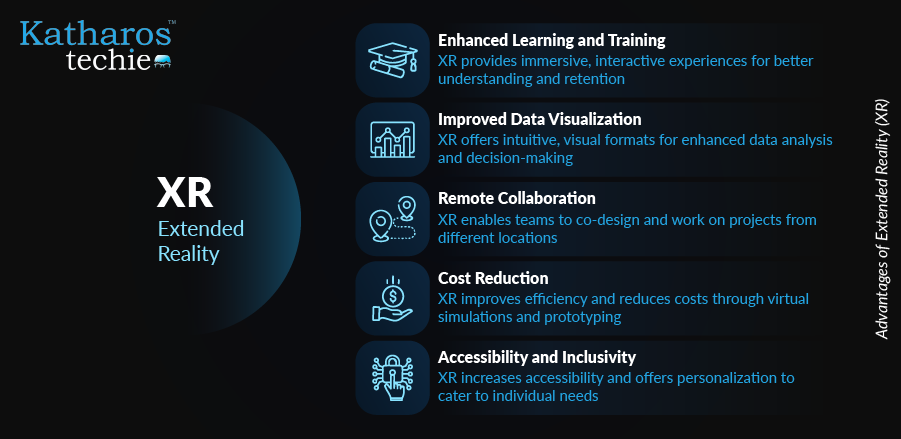
Extended Reality (XR) offers a multitude of advantages across various sectors by creating immersive and interactive experiences. From enhancing training programs to facilitating remote collaboration, XR technologies transform how businesses operate and individuals interact with information. Below are some key advantages of integrating XR solutions:
- Enhanced Learning and Training: XR provides immersive and interactive training environments. Medical students can use VR for surgical simulations to refine their skills in a low-risk digital setting. Construction workers can train in safe virtual environments, preparing them for real-world scenarios without the danger of on-site accidents.
- Improved Data Visualization: XR enables the 3D visualization of complex data, making it easier to understand and analyze. Scientists can use XR to visualize molecular structures, gaining insights that would be difficult to achieve with traditional methods. Engineers can inspect product designs in a virtual space, identifying potential issues and optimizing designs before physical prototypes are built.
- Remote Collaboration: XR facilitates real-time interaction in virtual environments, allowing teams to collaborate effectively regardless of their physical locations. Design reviews and virtual meetings enhance productivity, as participants can interact with 3D models and data in a shared virtual space. This technology reduces travel expenses and strengthens team cohesion by enabling seamless communication and collaboration.
- Cost Reduction: XR reduces expenses related to physical prototypes, as designs can be tested and refined in a virtual environment. Virtual training decreases the need for real-world resources, such as equipment and materials, leading to significant cost savings. Remote assistance lowers travel costs and downtime, as experts can provide guidance and support anywhere.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: XR provides customized experiences that cater to a wide range of users, including people with disabilities. People with disabilities can access virtual environments, participating in activities and experiences that might otherwise be inaccessible. Remote tourism and cultural experiences become available, allowing users to explore the world from the comfort of their homes.
These advantages highlight the transformative potential of XR. As the technology matures, its integration into various industries will continue to drive innovation and improve operational efficiencies, ultimately leading to a more connected and efficient world.
Market Growth and Future Trends of Extended Reality
The XR market is booming with the current technological advancements. It is expected to grow from USD 24.42 billion in 2024 to USD 84.68 billion by 2029, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.3%. This data underscores the rapid adoption of XR functionalities fueled by increasing consumer demand and expanding enterprise applications.
Future trends point towards more immersive and accessible XR experiences. Below mentioned are some of the key trends:
- Advancements in Hardware: Expect lighter, powerful headsets that improve user comfort and performance. Its high-resolution displays will further improve realism and visual quality in XR. In addition to that, integration of Haptic tech will also create more realistic interactions with virtual environments.
- Expansion of the Metaverse: XR is key to developing immersive virtual worlds for users. Future advancements will make virtual social platforms more intuitive and community-oriented. Decentralized platforms and digital identities could further define the future metaverse.
- Hyper-realistic Virtual Reality: VR may soon mimic reality, blurring the lines between real and virtual. Sensory VR will elevate immersion for unprecedented user experiences. Thus, making the digital platform feel like the physical world around it.
- WebAR Accessibility: WebAR makes AR accessible through web browsers and increases access. The technology is more compatible, and user-friendly across devices for all. Users can also expect greater adoption with simplified XR experiences.
These trends highlight the exciting trajectory of XR, promising a future where digital and physical realities are seamlessly integrated. As technology evolves, we can anticipate further innovations that enhance user experiences and unlock new possibilities across industries.
Final Thoughts
XR technologies are revolutionizing industries, and transforming how we interact with the digital world. From early stereoscopes to sophisticated VR/AR systems, XR’s journey has been marked by rapid innovation. As hardware improves and new applications arise, XR’s influence will continue to grow. Whether seeking business solutions or enhanced personal experiences, XR offers unprecedented opportunities. Ready to unlock the potential of XR for your business or personal use? Explore the latest XR solutions and discover how immersive technology can transform your world. Dive in and start your XR journey today.