
Machine Customers: The Future of Automated Commerce
By Ankita Das

The rise of machine customers is reshaping commerce, with market growth expected to increase from USD 1.4 billion in 2023 to USD 8.2 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 40.2%. Machine customers utilize artificial intelligence to purchase goods and services autonomously. This transformation demands businesses adapt their operations and marketing strategies. Unlike traditional customers, these systems operate on data-driven insights and algorithms. They prioritize speed, accuracy, and efficiency over human-centric experiences. Companies must understand these entities to remain competitive in the evolving marketplace. As machine customers become prevalent, their influence on purchasing decisions will only grow. Understanding their behavior is crucial for leveraging this new customer type effectively.
What is a Machine Customer?
A machine customer is an automated entity that utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to autonomously conduct transactions, such as purchasing goods and services. Unlike traditional automated systems, which operate strictly under predefined rules, these systems can learn from their interactions and adapt their behaviors based on data analysis. This adaptability allows them to make informed decisions, optimizing their purchasing processes without human intervention.
This technology typically evolves through three distinct phases. The three distinct phases are bound, adaptable, and autonomous. Each phase represents a progression in these automated entities’ capabilities and decision-making autonomy.
- Bound Phase: In this initial stage, the systems operate under strict rules defined by humans. They cannot deviate from these parameters, relying solely on preset instructions.
- Adaptable Phase: As machine customers progress to this phase, they analyze real-time data to make decisions. This flexibility allows them to respond dynamically to their environment.
- Autonomous Phase: In this phase, the system operates independently without human input. They make complex purchasing decisions based on comprehensive data analysis and predictive algorithms. This level of autonomy represents the pinnacle of machine customer evolution, where machines act as independent economic agents.
These phases illustrate how machine customers evolve from basic automation to sophisticated decision-making entities. As technology advances, the capabilities of this technology will expand further, leading to profound changes in how businesses engage with their market.
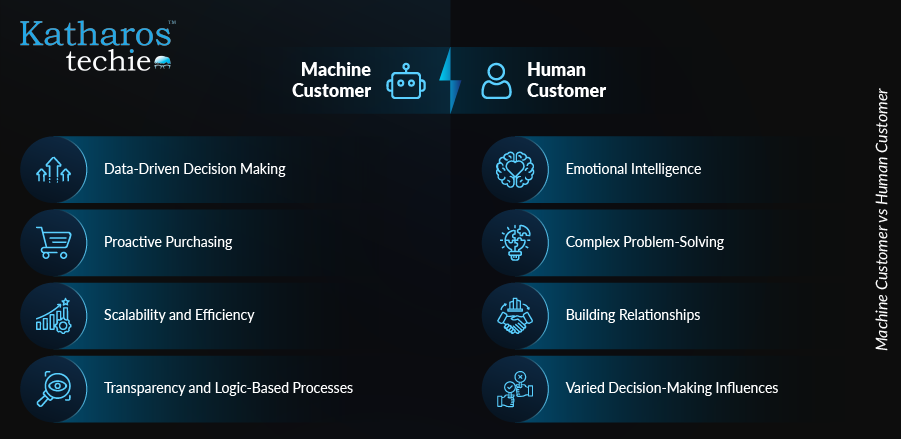
How do Machine Customers Differ from Human Customers?
Machine customers exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from human customers. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage the benefits of automation and AI in their operations.
| Aspects | Machine Customer | Human Customer |
| Decision-Making Process | Driven by data analytics and algorithms. | Influenced by emotions, preferences, and biases. |
| Availability | Operate 24/7 without fatigue. | Limited by human working hours and personal schedules. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Focus on efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and data-driven insights. | Rely on brand loyalty and emotional connections. |
| Data Processing | Capable of analyzing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. | Limited in processing information at scale; slower decision-making. |
| Transaction Speed | Execute transactions rapidly, enhancing operational efficiency. | Transactions may take longer due to deliberation and emotional factors. |
| Adaptability | Can adapt to changing market conditions in real-time. | Personal experiences and external factors influence adaptation. |
| Loyalty Drivers | Loyalty is based on efficiency and seamless processes. | Loyalty often stems from emotional satisfaction and trust in brands. |
How Machine Customers Impact Operations?
The integration of machine customers significantly impacts business operations across various sectors. Firstly, they enhance operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as inventory management and order processing. For instance, Amazon uses AI-driven systems to manage stock levels and automatically reorder items when they fall below a certain threshold.
Secondly, these systems enable businesses to gather valuable insights into consumer behavior through data analysis. This information can inform marketing strategies and product development decisions. Retailers can optimize their offerings based on purchasing patterns observed through machine customer transactions.
Additionally, the presence of machine customers necessitates changes in customer service approaches. Companies must invest in technologies that facilitate seamless interactions between human representatives and machine customers. This shift can lead to improved customer satisfaction as responses become faster and more accurate.
Future Trends of Machine Customers
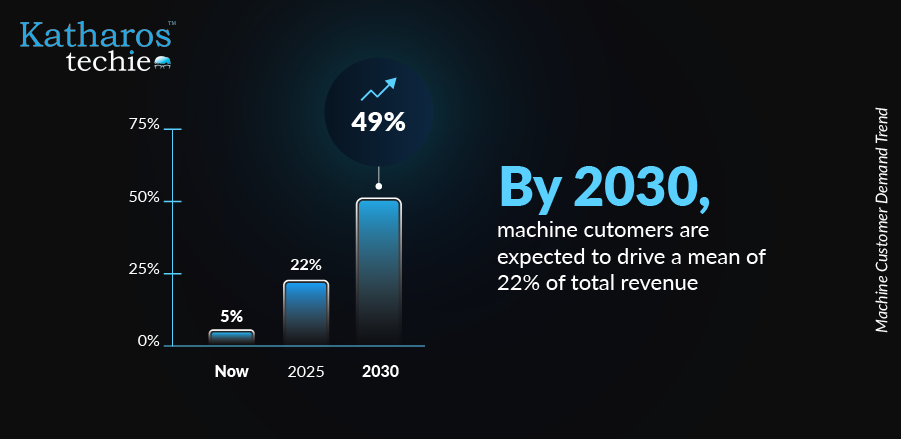
By 2030, machine customers are predicted to generate trillions of revenues. According to Gartner, CEOs believe 20% of their companies’ income could come from these technologies by then. Additionally, it is estimated that over 15 billion connected devices will be able to act as customers, changing how we think about shopping and transactions. As these technologies advance, machine customers will likely take on a larger role in everyday purchases, especially for routine items.
As machine customers evolve through different stages—from basic functions to more complex decision-making—they will increasingly influence how businesses sell products and services. This change will require companies to rethink their marketing strategies and operations to meet the needs of machine and human customers.